|
 |
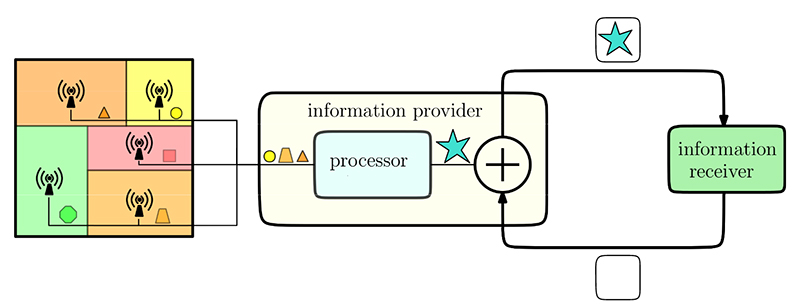
Diagram of an information updating system: an information provider (transmitter) that collects/processes data, and an information receiver. Figure from the paper. |
|
Age of Information for Updates with Distortion: Constant and Age-Dependent Distortion Constraints is a new paper by Professor Sennur Ulukus (ECE/ISR) and her Ph.D. student Melih Bastopcu that considers an information update system where an information receiver requests status updates from an information provider (transmitter) to minimize its age of information. Examples of such systems can be found in sensor networking and distributed computing applications.
Updates are generated at the transmitter in a process that involves completing a set of data collection and computation tasks. The distortion in each update decreases with processing time during the transmitter’s update generation. Longer processing generates a better-precision update, but increases the age of information—a trade-off between the information quality and freshness.
Ulukus and Bastopcu designed a system that strikes a desired balance between information quality and freshness by solving for the optimum update scheme subject to a desired distortion level. They modeled the quality of an update as an increasing function of the transmitter’s processing time spent while generating the update, using distortion as a proxy for quality, and model distortion as a decreasing function of processing time.
Subject to a minimum required quality/maximum allowed distortion constraint on the updates, the researchers determined age-optimal policies for the receiver’s update request times and the transmitter’s update processing times.
The researchers considered a case where the maximum allowed distortion is a constant that does not depend on the current age, and a case where the maximum allowed distortion depends on the current age. In the second case, they considered two sub-cases, where the maximum allowed distortion is an increasing function or a decreasing function of the current age.
Related Articles:
Five Clark School authors part of new 'Age of Information' book
Alum Ahmed Arafa wins NSF CAREER Award
Bastopcu and Ulukus build model for real-time timely tracking of COVID-19 infection and recovery
Buyukates and Bastopcu win Best Student Paper Award at IEEE SPAWC 2021
Who should Google Scholar update more often?
Ephremides leads new NSF Age of Information project
Barg honored with 2024 IEEE Richard W. Hamming Medal
Barg is PI for new quantum LDPC codes NSF grant
Narayan receives NSF funding for shared information work
Forthcoming information-theoretic cryptography book co-written by alum Tyagi and former visitor Watanabe
January 7, 2020
|

