|
 |
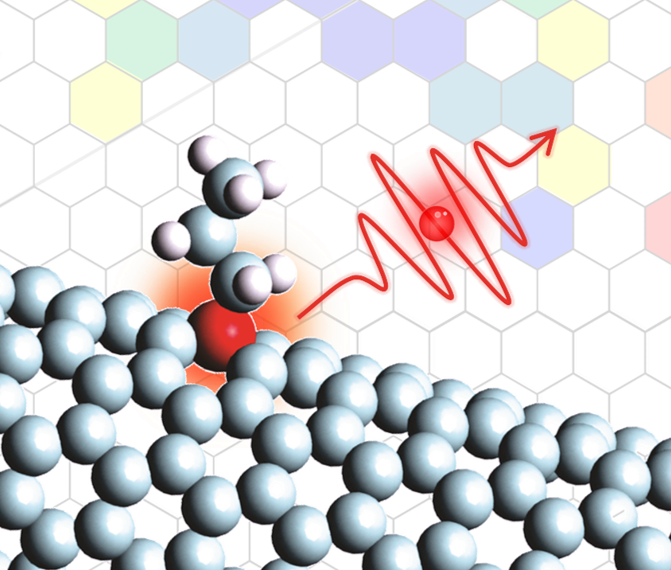
This artist’s rendition depicts a single photon busting from an organic color center, which was chemically created in a carbon semiconductor host. A new $1M NSF grant will fund research at UMD on color centers in carbon nanotubes as single-photon sources. Image credit: YuHuang Wang and Mijin Kim |
|
A team from the University of Maryland has been awarded $1 million by the National Science Foundation (NSF) to develop methods for generating single photons at room temperature in semiconducting carbon nanotubes. The project, which could result in new interfaces between electronic circuits and photonic devices, is part of a $31 million NSF effort to fund transformational quantum research that will enable the United States to lead a new quantum technology revolution.
NSF funded the project, “Integrated Circuits of Single-Photon Sources from Organic Color-Centers,” as part of an initiative known as Research Advanced by Interdisciplinary Science and Engineering—Transformational Advances in Quantum Systems (RAISE-TAQS). RAISE-TAQS is designed to encourage scientists to pursue exploratory, cutting-edge concepts in quantum research.
"Single-photon sources are a fundamental element for quantum information science and technology. However, it has been extremely difficult to prepare single photons with high efficiency,” said YuHuang Wang, a professor of chemistry and biochemistry at UMD and the principal investigator of the grant. “If successful, this work may further lead to a high-quality single-photon source that can be integrated directly into solid-state devices for photonic quantum information processing."
The award, which provides four years of funding, will leverage UMD’s expertise in quantum materials chemistry, theoretical physics, engineering, and quantum information science. In addition to Wang, the grant also has two co-principal investigators: Joint Quantum Institute (JQI) Fellow and Physics Adjunct Professor Charles Clark and JQI Fellow and Electrical and Computer Engineering Professor Edo Waks. Waks also has an appointment in the Institute for Research in Electronics & Applied Physics (IREAP).
The project will also make use of ongoing collaborations with Los Alamos National Laboratory and IBM. Through these collaborations and within the participating units at UMD, the award will also enable opportunities for graduate training in quantum information science and technology.
For the project, Wang, Clark, and Waks proposed a new way to generate single photons using crystallographic defects known as “color centers.” These imperfections occur naturally in some crystals. However, systems based on natural color centers can be unreliable and inefficient when used to generate single photons. To address these issues, the team proposed a method to engineer carbon nanotubes with a new family of color centers, discovered in the Wang lab, which can be chemically controlled with molecular-level precision.
In addition to providing a precise and reliable way to generate single photons, carbon nanotubes designed with color centers may also prove to be ideal desktop atomic physics laboratories, according to the researchers. Such applications could prove invaluable for studying the behavior of exotic “quasi-particles” such as excitons and trions.
The UMD award is one of 25 RAISE-TAQS projects, which will help lead to systems and proof-of-concept validations in quantum sensing, communication, computing, and simulations. In addition to the RAISE-TAQS program, which accounts for $25 million of the total $31 million awarded for quantum research, NSF also made an additional $6 million in grants via the related Research Advanced by Interdisciplinary Science and Engineering-Engineering Quantum Integrated Platforms for Quantum Communication (RAISE-EQuIP).
“The quantum revolution is about expanding the definition of what’s possible for the technology of tomorrow,” said NSF Director France Córdova. “NSF-supported researchers are working to deepen our understanding of quantum mechanics and apply that knowledge to create world-changing applications. These new investments will position the U.S. to be a global leader in quantum research and development and help train the next generation of quantum researchers.”
Related Articles:
Anticipation Builds as Zupnik Hall Nears Completion
Clean Energy critical for quantum/AI
NSF Awards Advances ISR Alum Research in Quantum and Brain-Inspired Computing
Barg honored with 2024 IEEE Richard W. Hamming Medal
Barg is PI for new quantum LDPC codes NSF grant
New quantum framework yields generalizations of bosonic ‘cat codes’
Thoughts from Rance Cleaveland on his time at the National Science Foundation
$1M NSF award supports reimagining cryptography in a post-quantum world
Dana Dachman-Soled is Program Chair for ITC 2022
From Innovation to Inauguration
September 26, 2018
|

