 |
|
 |
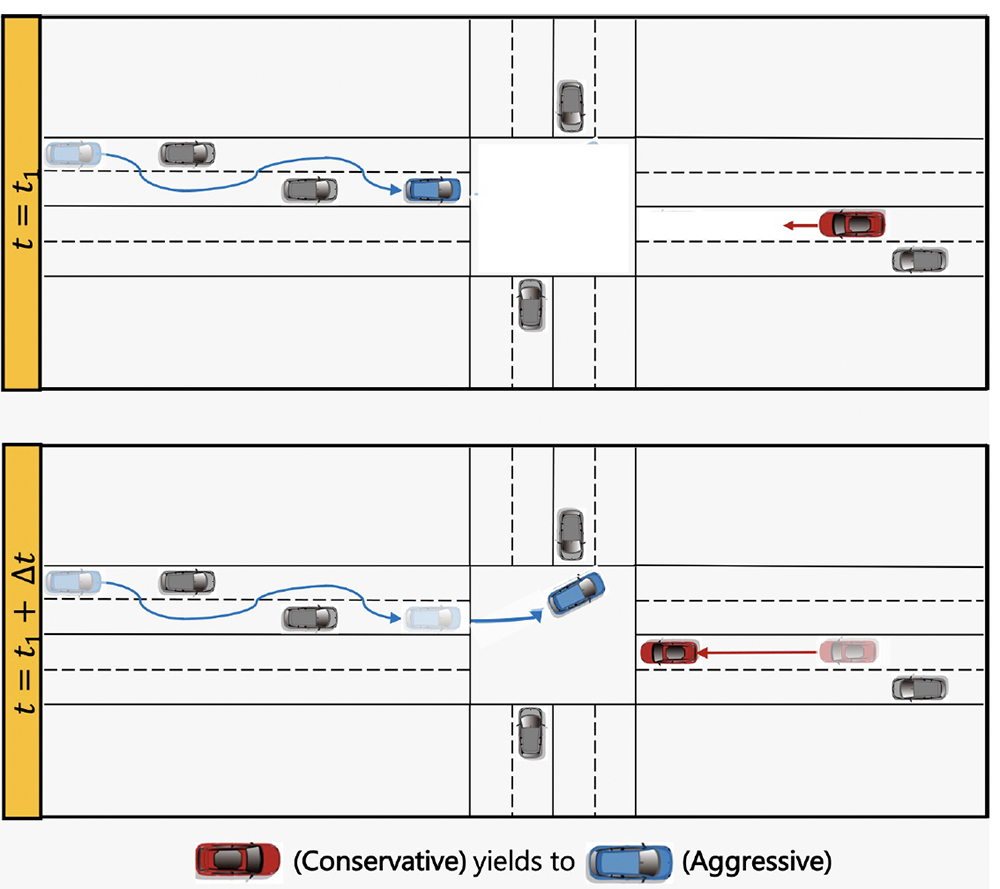
Risk-aware planning with human agents: The researchers’ risk-aware planner takes human driver behavior into account. In the ?rst step (top), the human agent is characterized either as aggressive (blue agent) or conservative (red). In the second step (bottom), the corresponding risk sensitivity of the human agent is derived, and the planner generates a game-theoretically optimal and safe risk-aware trajectory for the red agent that suggests the red agent yields to the blue human driver, allowing it to cross ?rst. (Fig. 1 from the paper) |
|
Human drivers are risk-aware by nature. For example, aggressive drivers frequently speed, overtake, and perform sharp cut-ins, whereas conservative drivers drive more cautiously. To navigate successfully among human drivers, autonomous vehicles (AVs) must be able to identify these risk preferences. Then AVs need to predict and plan future motion by taking their own and human drivers’ preferences into account.
“Game-Theoretic Planning for Autonomous Driving among Risk-Aware Human Drivers” presents a novel approach for risk-aware planning with human agents in multi-agent traf?c scenarios. It was written by ISR-affiliated Professor Dinesh Manocha (ECE/UMIACS), his Ph.D. student Rohan Chandra (CS), and Stanford University’s Mingyu Wang (Mechanical Engineering) and Mac Schwager (Aeronautics and Astronautics). Their approach takes into account the wide range of human driver behaviors on the road, from aggressive maneuvers like speeding and overtaking, to conservative traits like driving slowly and conforming to the right-most lane.
The approach learns to map from a data-driven human driver behavior model called “CMetric” to a driver’s entropic risk preference. The researchers then use the derived risk preference within a game-theoretic risk-sensitive planner to model risk-aware interactions among human drivers and an autonomous vehicle in various traf?c scenarios.
Their results show that aggressive human driving results in more frequent lane-changing. They show that conservative drivers generally yield to aggressive drivers while maintaining a greater distance from them. The researchers also con?rm that the ?nal trajectories obtained from the risk-aware planner generate emergent behaviors that participants in a companion study can recognize as either aggressive or conservative drivers.
In a merging scenario, the ?nal trajectories obtained from the risk-aware planner generate desirable behaviors. Particularly, the researchers’ planner is able to recognize aggressive human drivers and responds accordingly—both yielding to them and maintaining a greater distance from them.
Related Articles:
ASTrA project to provide new tools for power generation, robotics, smart manufacturing
Algorithm helps autonomous vehicles navigate common tricky traffic situations
Cornelia Fermüller is PI for 'NeuroPacNet,' a $1.75M NSF funding award
Zampogiannis, Ganguly, Aloimonos and Fermüller author "Vision During Action," chapter in new Springer book
The Falcon and the Flock
ArtIAMAS receives third-year funding of up to $15.1M
Autonomous drones based on bees use AI to work together
'OysterNet' + underwater robots will aid in accurate oyster count
Helping robots navigate to a target, around obstacles and without a map
Which way should I go?
June 21, 2022
|

