|
 |
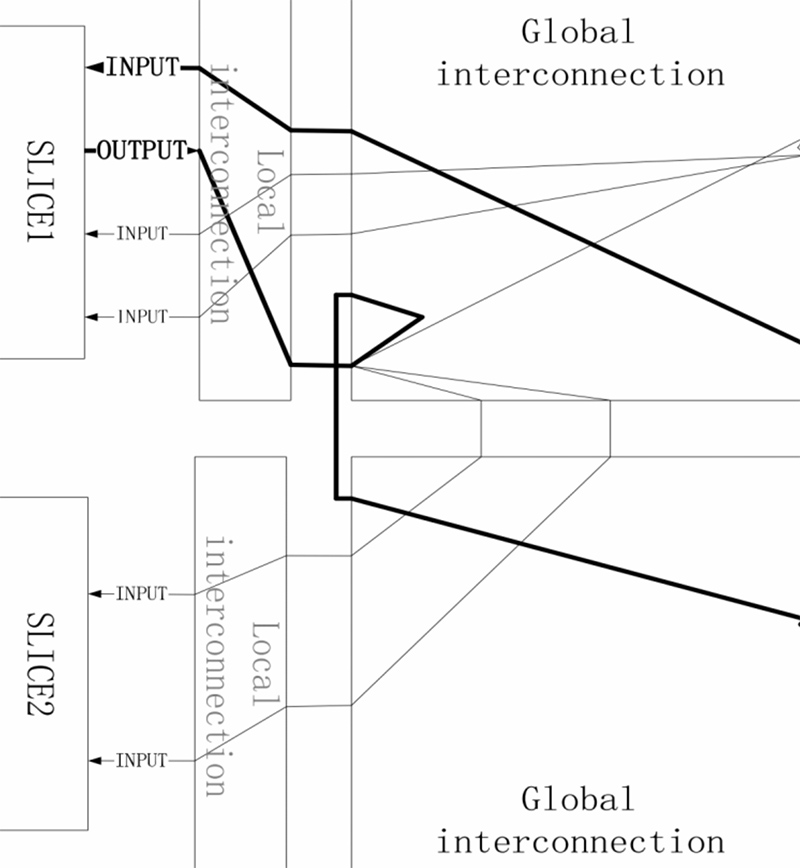
Signal transmission between slices (Fig. 1 from the paper) |
|
Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are integrated circuits designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturing.
While programmability is one of the great advantages of FPGAs, it also brings some difficulties to FPGA design. Because of the FPGA’s programmability, the type of circuit the end user will implement and its critical path are both unknown at the time of design. The critical path of FPGA can only be determined after programming, but the FPGA needs to implement different kinds of circuits. The representative path will differ based on how the circuit is implemented. This makes an FPGA challenging to optimize at the transistor level.
To handle the issue, researchers create a representative path to use during optimization. This is the shortest register-to-register path within an FPGA that contains all unique components. Research to date has not analyzed how different reference circuits can affect the representative path.
In “Research on the impact of different benchmark circuits on the representative path in FPGAs,” Professor Gang Qu (ECE/ISR) and his academic colleagues Jiqing Xu, Zhengjie Li, Yunbing Pang, Jian Wang, and Jinmei Lai explore the impact of different benchmark circuits on the representative path. They propose two methods to obtain the usage of interconnect and logical partial sub-circuits on critical paths. They also compare two aspects of the representative path and each critical path: the utilization rate of sub-circuits and the path delays. The statistical results show that the sub-circuit utilization rate on the representative path can indicate the usage of sub-circuits in different benchmark circuits, and the critical path delay of FPGA fluctuates in a small range of the representative path delay when implementing different benchmark circuits.
The authors found that the representative path delay can represent the average of the critical path delays under different reference circuits under the premise of selecting a large number of typical benchmark circuits. Under the premise of selecting a large number of typical benchmark circuits, the representative path delay can well represent the overall timing performance of FPGAs.
The work was presented at the 2019 IEEE 13th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON).
Related Articles:
New security method for integrated circuits developed by Srivastava-Northrop Grumman team
Srivastava wins NSF funding for integrated circuit fabrication security
New simulator models 3D DRAM thermal characteristics and timings
ECE Announces Computer Engineering Minor
Better 'lifetime predictions' for NAND flash memory
Deepfake Detection Invention Discerns Between Real and Fake Media
Improving Fairness and Trust in AI Used for College Admissions and Language Translation
PUF-based key holds promise for IC security
Securing IC encryption during manufacturing and testing
Warren Savage delivers cybersecurity keynote at DesignCon 2020
February 12, 2020
|

